Uniboob (Symmastia)

Introduction to Uniboob (Symmastia)
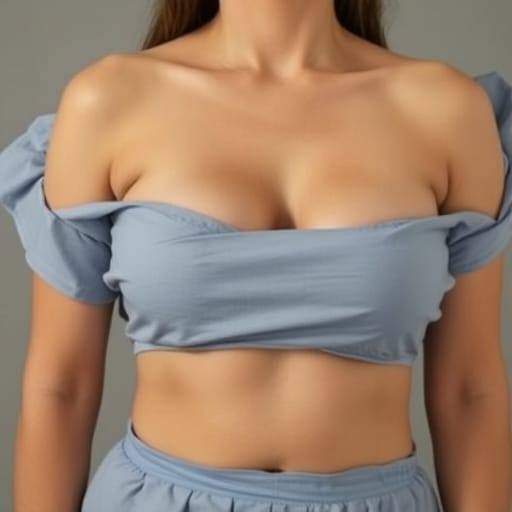
- Definition of Symmastia (Uniboob): Introduce the term "uniboob" or symmastia, a condition where the breasts appear to merge into one due to a lack of separation between the breasts. Explain its medical implications and describe how it affects the aesthetics of the chest area.
- Differentiating Between Congenital and Iatrogenic Symmastia: Detail the difference between congenital symmastia (present from birth) and iatrogenic symmastia (induced by surgical procedures). Discuss the factors that lead to each, emphasizing that congenital symmastia occurs due to genetic anomalies, whereas iatrogenic symmastia is the result of surgical error.
- Common Misconceptions About Uniboob: Discuss the common misunderstandings surrounding symmastia, such as the belief that it is solely caused by breast augmentation surgery or the assumption that it cannot be treated.
Anatomy of the Chest and Breast
- Understanding Normal Breast Anatomy: Provide an in-depth look at breast anatomy, including the chest muscles (pectoralis major and minor), the role of Cooper's ligaments, fat tissue, and skin. Explain how these structures interact to create natural breast separation.
- Role of the Chest Muscles, Ligaments, and Skin: Explore how each component contributes to the formation of the cleavage and support of the breasts. Highlight how healthy anatomy ensures a natural gap between the breasts.
- Breast Separation and the Natural Cleavage Zone: Define the "cleavage zone," explain how it varies between individuals, and emphasize the average anatomical distance between breasts.
- What Happens Anatomically in Symmastia (Uniboob): Illustrate the specific anatomical changes that occur in symmastia, such as the merging of breast tissue, displacement of implants, or laxity of the skin and muscles in the cleavage area.
Causes of Uniboob
- Congenital Causes: Discuss the genetic and developmental factors that lead to congenital symmastia, including underlying tissue defects, abnormal muscle attachment, or skin irregularities.
- Surgical Errors (Iatrogenic Causes): Examine how surgical errors, particularly during breast augmentation, can result in uniboob. Highlight poor preoperative planning, miscalculated cleavage creation, and implant misplacement.
- Breast Augmentation Complications: Detail how breast augmentation can lead to uniboob through improper implant size, over-dissection of tissues, or placing implants too close together.
- Use of Large Implants: Explore the risks associated with using overly large implants that stretch the skin and increase the likelihood of symmastia.
- Over-dissection of the Cleavage Area: Explain how surgeons can inadvertently cause uniboob by cutting too much tissue in the cleavage area during surgery, leaving the breasts without adequate separation.
- Capsular Contracture Contributing to Symmastia: Discuss how capsular contracture (a common breast augmentation complication) can worsen or lead to symmastia due to the tightening of scar tissue around the implant.
- Trauma and Injury-Induced Uniboob: Address the less common causes of symmastia, such as chest injuries or trauma that alters the structure of the breasts and cleavage area.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Visual and Physical Signs of Symmastia: Describe how patients can recognize symmastia, focusing on the visible signs of breast merging, loss of cleavage, and changes in breast shape.
- How Uniboob Affects Aesthetics and Appearance: Discuss the aesthetic concerns associated with uniboob, including how it impacts symmetry, proportion, and overall chest appearance.
- Diagnostic Techniques Used by Plastic Surgeons: Review the methods surgeons use to diagnose symmastia, including visual examination, palpation, and imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI to assess tissue and implant placement.
- Psychological Effects of Uniboob on Body Image: Explore the emotional and psychological impacts of symmastia, particularly on body image, confidence, and self-esteem.
Risks Associated with Breast Surgery
- Overview of Breast Augmentation Risks: Provide a broad overview of the general risks involved in breast surgery, such as infection, bleeding, scarring, and implant-related complications.
- How Surgical Practices Can Lead to Symmastia: Dive into specific surgical practices that can contribute to the development of symmastia, such as overly aggressive dissection or implant placement that does not respect the natural cleavage.
- Preventative Measures During Breast Augmentation: Offer a detailed look at what surgeons can do to avoid symmastia, such as proper preoperative planning, careful tissue handling, and respecting anatomical boundaries during surgery.
- Role of the Surgeon's Expertise in Avoiding Uniboob: Emphasize the importance of choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon to minimize the risks of developing uniboob.
Preventing Uniboob During Surgery
- Preoperative Planning to Avoid Complications: Discuss the critical role of thorough preoperative assessments, 3D imaging, and detailed planning in avoiding symmastia during breast surgery.
- Implant Placement and Techniques to Minimize Risk: Explain the different techniques surgeons use to place implants (sub-glandular, submuscular, dual-plane) and how each can affect the risk of developing symmastia.
- Subglandular vs. Submuscular Placement: Compare the pros and cons of placing implants either above or below the muscle, focusing on the associated risks of uniboob in each method.
- Appropriate Implant Size: Discuss how selecting the proper implant size can prevent symmastia by ensuring that the implants fit well within the patient's natural anatomy.
- Surgical Precision in Cleavage Creation: Highlight the importance of the surgeon's precision in creating cleavage, avoiding over-dissection or making too much space between the breasts.
- The Importance of Post-Surgical Care and Follow-Ups: Provide guidelines for post-surgical care, including wearing the fitting compression garments, monitoring the healing process, and attending follow-up appointments to prevent complications like uniboob.
Treatments and Surgical Corrections for Uniboob
- Options for Fixing Congenital and Post-Surgical Symmastia: Review the various options for correcting symmastia, whether congenital or caused by surgery, including surgical techniques like fat grafting and implant repositioning.
- Symmastia Correction Surgery: Detail the process of symmastia correction surgery, including what patients can expect during and after the procedure.
- Fat Grafting Techniques: Explain the use of fat grafting in uniboob correction, where fat is harvested from other parts of the body and injected into the cleavage area to improve breast separation.
- Revision Breast Augmentation Procedures: Discuss revision surgery for patients who developed uniboob after breast augmentation, including what goes into re-planning and executing a successful corrective procedure.
- Recovery Time and Post-Operative Expectations: Provide a timeline for recovery after uniboob correction surgery and explain what patients can expect during the healing process.
- Success Rates and Long-Term Results: Review the typical success rates of symmastia correction surgeries and discuss long-term results and the possibility of recurrence.
Non-Surgical Management of Symmastia
- Can Uniboob Be Treated Without Surgery? Explore whether non-surgical approaches to managing symmastia can be practical and in what circumstances they might be recommended.
- Role of Compression Garments and Support Bras: Discuss the use of specially designed bras and compression garments in managing mild cases of symmastia or post-surgery recovery.
- Exercises or Techniques to Manage Mild Cases: Explore whether specific exercises or therapeutic techniques can help manage or correct mild cases of uniboob.
- Role of Fillers in Treating Mild to Moderate Cases: Introduce the potential use of dermal fillers or fat injections as a non-surgical treatment for mild or moderate symmastia.
Choosing the Right Surgeon
- How to Find an Experienced Plastic Surgeon: Provide tips for finding the right plastic surgeon, including what credentials and experience to look for when choosing someone to perform uniboob correction.
- Importance of Board Certification: Emphasize the importance of selecting a board-certified plastic surgeon who has undergone the rigorous training and examinations required for certification.
- Questions to Ask Your Surgeon Before Undergoing Surgery: Suggest a list of critical questions patients should ask their surgeon before deciding to undergo breast surgery, including their experience with symmastia cases and expected outcomes.
- Surgeon Reviews, Portfolio, and Experience with Symmastia Cases: Encourage patients to research their surgeon's past work by looking at reviews, before-and-after portfolios, and case studies to assess their proficiency with symmastia correction.